What is pemphigus vulgaris?
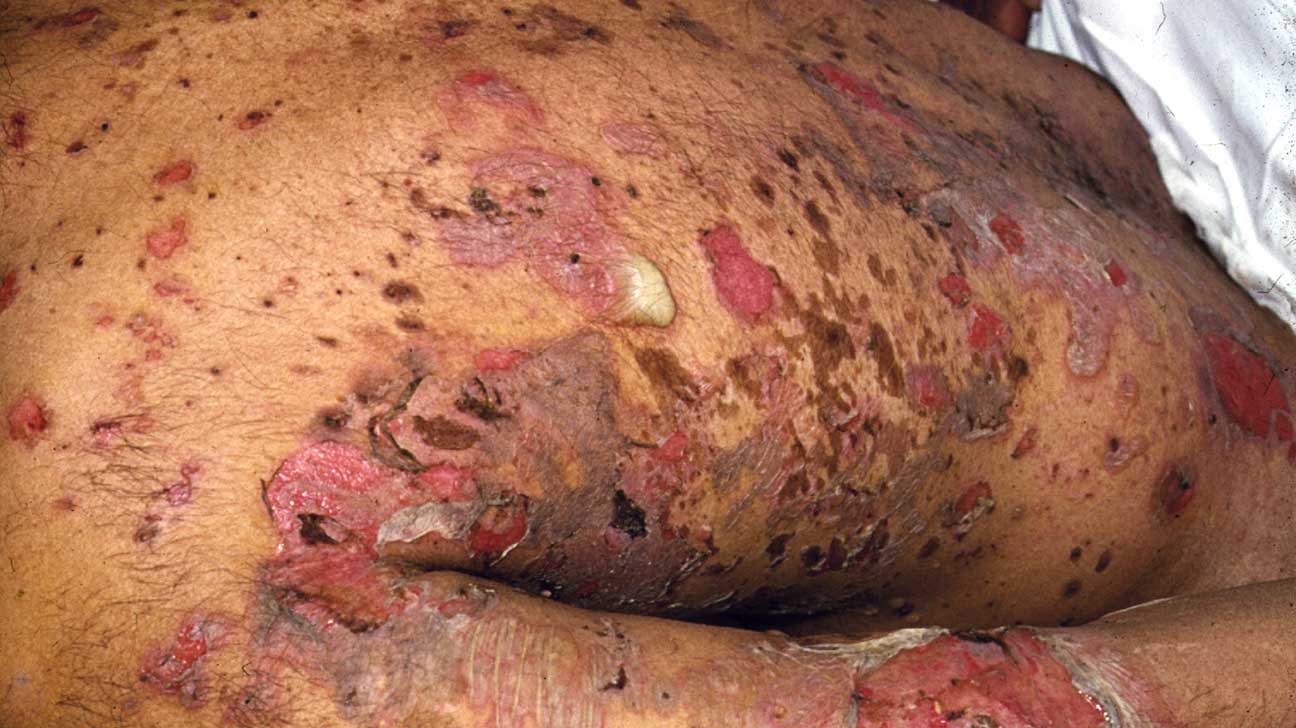
Pemphigus vulgaris is caused by immunoglobulin G (IgG) autoantibodies which bind to a protein called desmoglein 3. As clinical features, there are thin-walled flaccid blisters filled with clear fluid causing itchy and painful erosions. Darken erythematous crusted patch with some areas of blister and erosions can be seen on the back of the body.
Firstly, most patients present with lesion on mucous membranes (mouth, genitalia). Involvement of the pharynx and larynx may cause pain on swallowing and hoarseness of voice. Skin around the nail can be painful, red and swollen. Nasal involvement may cause congestion and bleeding. The conjunctiva, oesophagus, labia, vagina, cervix, penis, urethra and anus may also be affected.
We need to ask the following questions?
Drugs history (sulphur, penicillamine, NSAID, ACEI, beta-blockers, antipsychotic, rifampicin)
Viral infection (HSV, HCV, cosxakie, measles, herpes zoster)
Bacteria history (Mycoplasma, Syphilis, Meningococcal, Streptococcus)
Immunization such as influenza shot, HBV vaccine
What other features would be needed in clinical examination?
Nikolsky’s sign
Asboe-hansen sign
Oral mucosal involvement
Nail changes
Differential diagnosis
Bullous pemphigoid
Drug induced pemphigus
Linear IgA pemphigus
Fixed drug eruption
Varicella zoster
Steven-Johnson syndrome
Dermatitis herpetiformis
What key investigation would likely clinch the diagnosis?
Skin biopsy will confirm the diagnosis.

Write Reviews
Leave a Comment
No Comments & Reviews