Excisional biopsy
- removing the full lesion with surrounding normal tissue (including the adipose tissue) with 2mm clear margin
- Indication – Melanomas, Skin cancers and bullous lesions
- Method – elliptical incision (made with length three times the width with an angle of 30)
Note : used only in less than 2cm size lesions , not take in sensitive area (lips, eye, ear)
Incisional biopsy
- part of the lesion with a part of normal tissue is removed for comparison. (both epidermis and dermis)
- Indication – Granulomas, Lymphoid infiltrate, SCC
- Method – surgical cut is made through the skin to remove a sample of abnormal tissue or part of a lump on suspicious area.
Note : deeper incision is better than a wider one
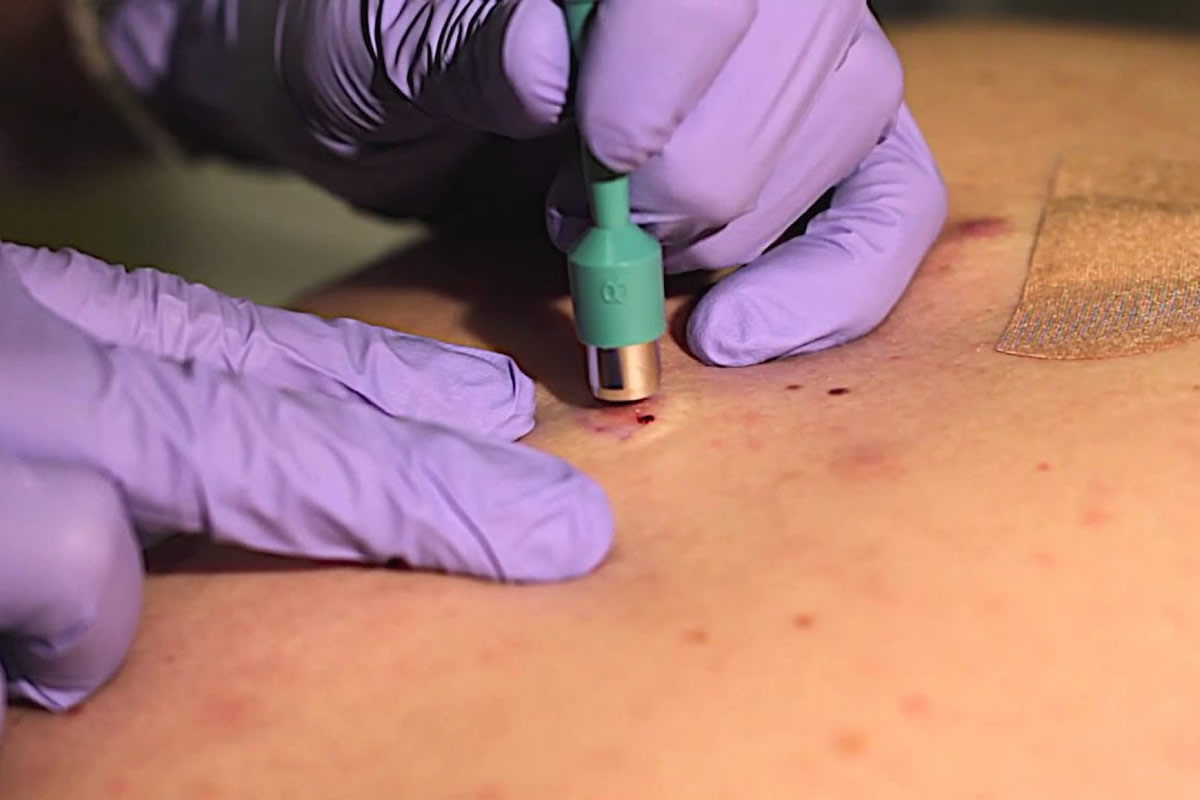
Punch biopsy
- full thickness skin biopsy (epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous)
- Indication – solid lesion , small vesicle, pyogenic granuloma
- Method – stretch the skin area first, then rotate the sharp cutting tool in circular motion to get a tube-shape piece of skin.
Shave biopsy
- superficial lesion (epidermis, papillary dermis)
- Indication – Seborrhoeic Keratosis, Naevi
- Method – 1mm depth of skin was shaved or taken by using blade (scalpel or razor), then apply aluminium chloride 20% solution (drysol) to control bleeding, but that will never be used in melanoma.
Important Notes
- Punch and shave biopsy – for benign lesion
- Excisional and incisional biopsy – for malignant lesion
Fine needle aspiration
- Indication – epidermal cyst, papulo-nodular lesions, BCC, SCC
- Procedure – to extract sample fluid or tissue from a cyst or a solid mass.
Dr. Aye Min Htoo
Dermatologist

Write Reviews
Leave a Comment
No Comments & Reviews